Great documentation is a team effort and our goal is to make it easy for everyone to collaborate seamlessly. At ReadMe, everyone at the company contributes to documentation. From technical writers to API engineers and marketers–working from ReadMe's UI or a GitHub repository–anyone can make edits to docs from anywhere.
By connecting your ReadMe project to your GitHub repository, your team can edit documentation from either platform and feel confident that their docs are always in sync.
In this blog post, I’ll show you how to get the value out of writing documentation from various places using ReadMe’s bidirectional sync with GitHub.
You will need:
- Admin access the ReadMe project you would like to connect to a GitHub repository
- Empty GitHub repository (public or private)
1) Connect Your ReadMe Project to a GitHub Repository
First you’ll connect your GitHub repository to your ReadMe project. You’ll need a new, empty repository. Navigate to Settings in the top left corner. Under Admin > Git Connection, click Sync with GitHub.
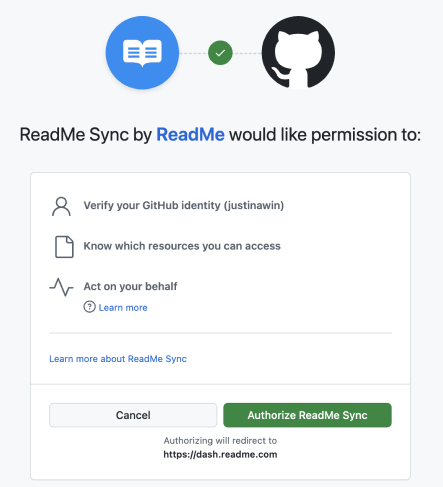
2) Then, you'll need to install the ReadMe Sync GitHub App.
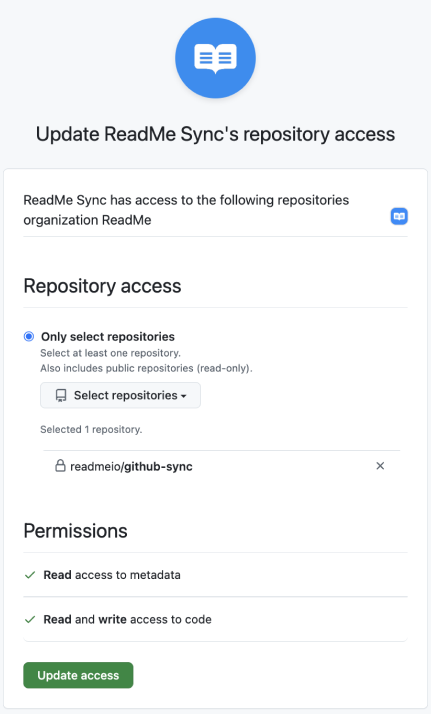
This is where you choose which organization you want to install the connection to and give granular permissions to a specific repository with read/write access.
3) After, you'll choose which repository you want ReadMe to sync to. It’ll sync through all of the content.
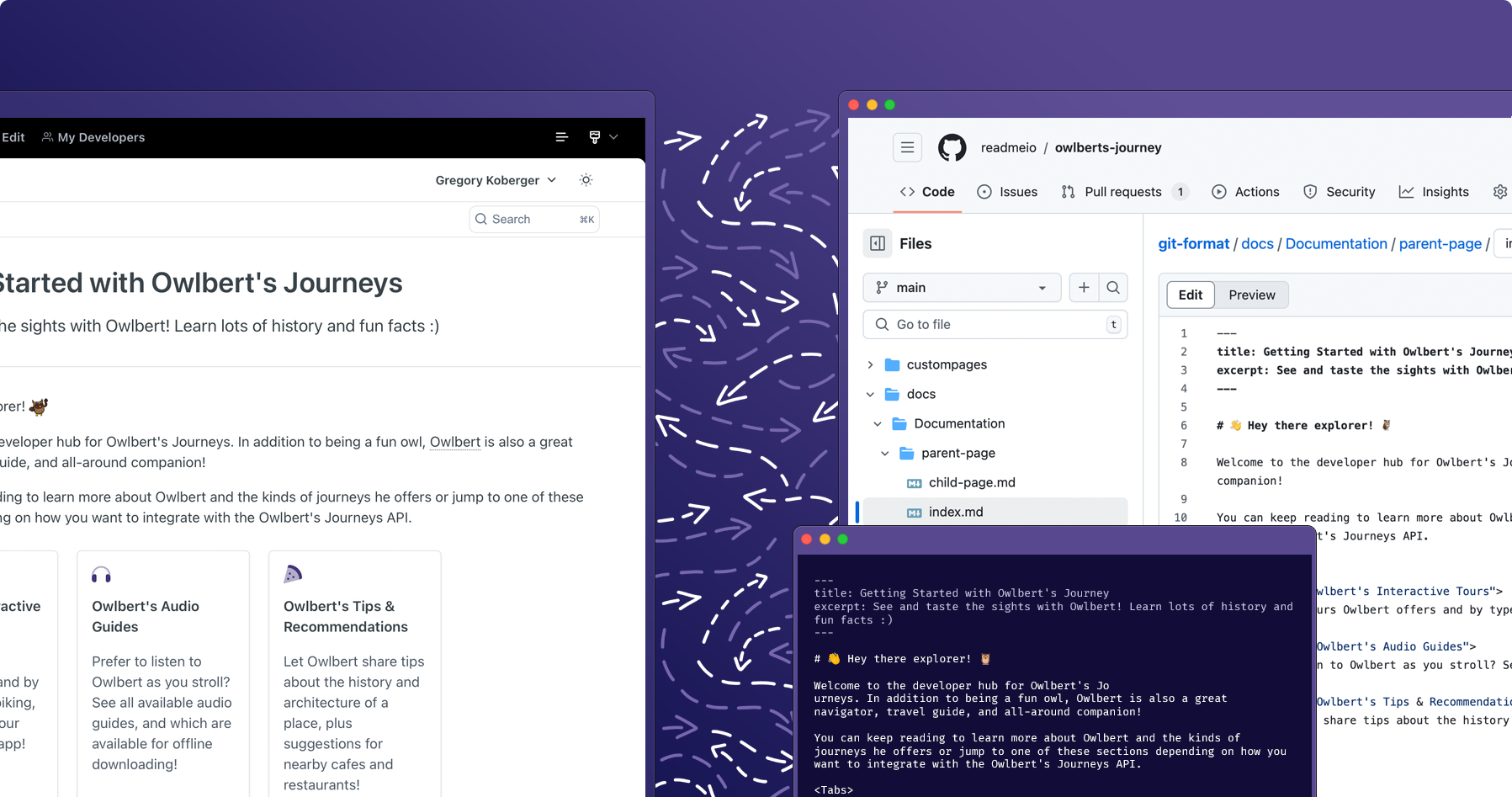
How ReadMe Content is Structured in GitHub
After connecting your ReadMe project to your GitHub repository, you'll notice that bi-directional sync provides a format that closely mirrors your ReadMe project structure. There is a top-level docs folder where you’ll see your Guides. Each category in ReadMe is a folder in GitHub. When you click into folders, you can see the individual pages. The ordering of ReadMe pages is reflected by an order.yaml file in GitHub. We have a Reference top-level folder where the OAS files and endpoint pages from your API Reference are stored.
4) Start Writing Docs in Either Platform
In ReadMe, switch to Edit Mode to make a change. That change will automatically sync to GitHub within a few seconds. No matter where a change is made—in ReadMe or GitHub—you can view the full edit history in GitHub.
You can also see the individual commits and their diffs.
You can also make edits directly in GitHub by clicking into a folder and committing those changes. Within a few seconds, you can go back to View Mode in ReadMe to see those changes you pushed. If you prefer to work in GitHub’s desktop app, you can clone the repository down to your machine and make edits there before committing them back to the main branch.
Versioning Support
Versions are defined as branches in GitHub like v4.0, is a v4.0 branch. Each documentation version corresponds to a Git branch. The default branch represents your main version.
Hope this was helpful! Check out our docs with details on configuration to get started. If you have any feedback, feel free to reach out to me directly in our Slack community!